Overview of the agile project management framwork Scrum, and its main pillars and values: Sprint scrum, scrum master, product owner, daily scrum meeting, scrum board…
What is the Scrum method?
Scrum is the most widely used agile framework. Like other agile methods, Scrum is a project management approach that makes the customer (or user) the main driver of the team in charge of developments. Historically, it is mainly implemented in the IT domain, and in the application development domain in particular. However, it is also used more and more in other areas of product engineering.
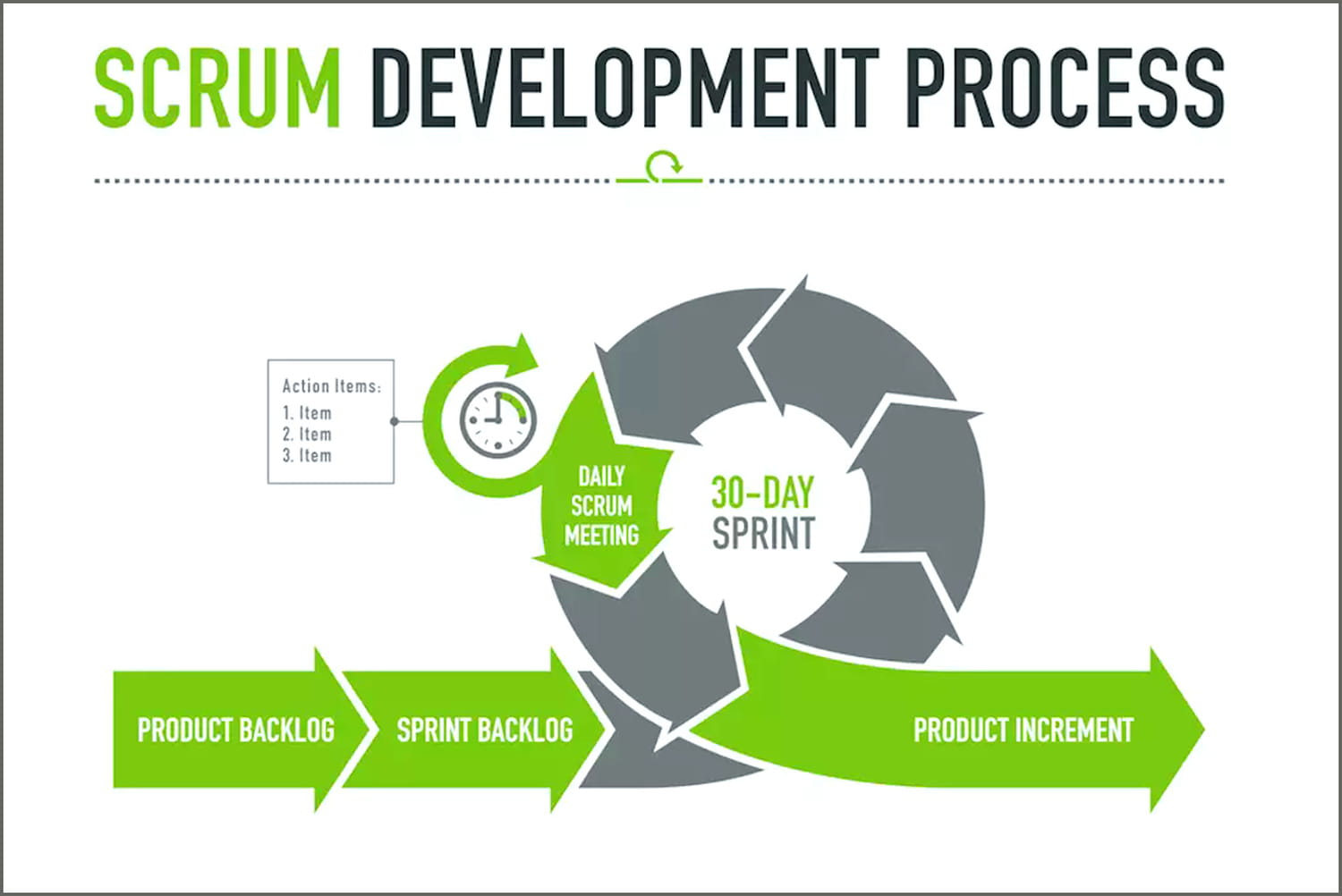
The term “scrum” means “scrimmage” and is openly inspired by rugby, a sport that requires a close-knit team moving in the same direction. In the Scrum Method, a “scrum” is a sprint. This means a development phase of one to four weeks that aims to focus the project team on a limited part of the product or service to be delivered. Typically, it will be a matter of concretizing some functionalities in the case of an application. At the end of each sprint, a sprint review is organized to review the progress of the project with the members of the project team, to examine the possible adaptations to be made, and to identify the objectives of the next sprint (see the infographic below).
What is the main contribution of Scrum?
Like other agile methods, the main advantage of Scrum is that it quickly leads to a first iteration of a product or service that can be used in the field. Validated progressively by the customer, the following sprints allow to enrich this first base. Result: project management becomes a much more productive process.
Gone is the tunnel effect of V-cycle projects that start with the analysis of requirements and then move on to specification, design, coding and testing. Projects that are characterized by a single delivery at the end of the process that may no longer fit with the business issues that will have evolved in the meantime.
What is a scrum sprint?
The sprint is the centerpiece of the Scrum agile method. Hence the commonly used name of sprint scrum. Sprints are short development iterations designed to create a product or service in an incremental way.
What are the 3 pillars of Scrum?
Scrum determines a framework to facilitate the rapid and efficient implementation of a development project. To successfully apply this framework, Scrum recommends three fundamental pillars :
- Transparency. It aims to ensure that the stakeholders (project team, management and users) share a common language and benefit from all the information necessary to understand the project.
- Inspection. The purpose of inspection is to check, through regular evaluations, that the development is still in line with the customer’s requirements and that it does not deviate from them.
- Adaptation. A concept that lives up to its name. Its objective? To correct the project’s trajectory if deviations from the results to be achieved are detected during the inspection phase.

What are the five values of Scrum?
To these three pillars, the Scrum infrastructure adds five values aimed at making the work effective and the collaboration between the actors in presence fluid and in line with the objectives to be achieved:
- Focus. The project team must be fully focused on the development to be achieved.
- Openness. The project team as well as the management must be open to the Scrum way of working, in particular to interpersonal communication to move forward and solve problems together.
- Respect. All stakeholders (project team members, management and customers) must show mutual respect.
- Courage. Finally, the project team must have the courage to meet the challenges it will face independently.
- Commitment. This is a value that also contributes to the success of the process. Scrum team members must be personally committed to achieving the goals of each sprint.
Focus, openness, respect, courage and commitment form the acronym Force which illustrates the purpose sought through these four core values by the Scrum agile method.
What are the 6 principles of Scrum?
In addition to its three pillars and these five values, Scrum puts forward five operational principles:
- Empirical process control,
- Autonomy and self-organization of the team.
- Collaboration.
- Prioritization or value-based prioritization.
- Due dates,
- Iterative development.
What is the role of the scrum master?
Scrum recommends appointing what it calls a scrum master. His role is to guarantee the implementation of the agile framework and to manage the four stages of a scrum sprint: planning, daily meeting, sprint review and sprint retrospective. The scrum master is a central element for the smooth running of the project team and is also the guarantor of the fluidity of exchanges and the productivity of work. As such, he/she identifies blocking points and leads brainstorming sessions to identify solutions. Finally, he/she writes the burndown chart (BDC) that describes the volume of tasks remaining to be completed on the vertical axis and the projected timing on the horizontal axis.
Faced with these challenges, a scrum master is expected to master the Scrum infrastructure. He or she must also demonstrate pedagogy and opt for a participative management style based on coaching. From this point of view, the role of srcum master will most often be assigned to the project manager.
What is the salary of a scrum master?
The salary of a scrum master is higher than that of an average IT project manager. Indeed, a scrum master is expected to combine the skills of a project manager with those of a coach and team leader. All this combined with an excellent knowledge of Scrum.
The scrum master can have acquired the mastery of the Scrum method by practice or by following a training leading to a scrum master certification.
What is the role of the product owner?
Alongside the scrum master, Scrum advises to appoint a product owner. His mission? Representing the customer within the project team, he is the guarantor of the product vision. He is responsible for feeding the project backlog with items or business functionalities to be implemented, with detailed specifications for each one. In Scrum language, these items are called user stories. They describe the customer’s needs in simple language that can be understood by all stakeholders.
Within the backlog, the product owner prioritizes the user stories according to four criteria: the business value introduced, the technical and business knowledge required for implementation (need for training?), the effort to be produced by the project team, and the risks, i.e. the associated constraints that may generate imponderables (technical and business prerequisites, solicitation of a supplier, etc.)
The product owner’s mission is therefore to integrate both the users’ requests and the technical constraints linked to the implementation. At each stage of the project, or sprint, he is responsible for presenting the work done to the customer. He/she analyses the feedback with the project team to ensure that the product or service developed corresponds to the client’s expectations and that it remains within the budget. To facilitate user feedback, Scrum recommends setting up user tests at the end of each sprint.
What is a daily scrum meeting or daily scrum?
The daily scrum is a meeting that takes place during a sprint. It allows each member of the project team to review the tasks completed the day before and those to be completed during the day. It is organized in front of the scrum board, which takes stock of the current sprint.
Not to exceed 15 minutes, the daily scrum meeting is also an opportunity to discuss blocking points and possible solutions to resolve them. If a debate is launched on a thorny issue, Scrum advises to plan a meeting dedicated to the subject and limited to the people concerned.
What is a scrum board?
The scrum board (or scrum task board) is a board inspired by the Kanban method. It allows you to follow the progress of tasks within the current Scrum sprint.
Most often deployed on a whiteboard, the scrum task board is divided into at least three columns: tasks to do, tasks in progress and completed tasks. Squares of adhesive paper representing these tasks will be moved from one column to another as the sprint progresses. Depending on the needs, intermediate columns can be added (test, recipe…).
Originally Scrum, Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland are the authors of the Scrum Guide which lays the foundations of the agile method of the same name. Foundations, pillars, values, roles, meetings… It reviews the different concepts of the framework.
Independent from any software publisher or service provider, the Scrum Guide is available on the web. It can also be downloaded from Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland’s website (Scrum.org):
Originally, it was Ken Schwaber who laid the foundations of what would become the Scrum method during a conference in 1995. He then detailed the principles in an article published in 1996 in the Cutter Business Technology Journal (article entitled Controlled Chaos: Living on the Edge).
What are the missions of the Scrum Alliance?
Founded in 2001, the Scrum Alliance is a non-profit organization whose mission is to promote the agile movement through certifications. Led by members of the agile community, it fuels debate and research in this field.
What are the scrum master certifications?
There are several recognized certifications in this field. They aim to validate and label Scrum skills. Historically, the Scrum Alliance was the first non-profit organization to offer certification training in this field. There are three levels: Certified ScrumMaster, Advanced Certified ScrumMaster and Certified Scrum Professional ScrumMaster. The same logic applies to the product owener via Certified Scrum Product Owner, Advanced Certified Scrum Product Owner and Certified Scrum Professional Product Owner.
In france, Agilbee, a training company specialized in agile methods, offers the Scrum Alliance courses and certifications in French. The Scrum League’s Scrum certifications are also available in French.
The main alternative to the Scrum Alliance’s offer is Scrum.org, which has also set up Scrum certifications, particularly through the Professional Scrum Master and Professional Scrum Product Owner programs. Available only in English, they have the advantage of having been designed directly by the authors of Scrum, Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland.
Scrum vs Kanban
Often put in competition, the Scrum and Kanban agile methods are much more complementary than they seem. The first aims to split product development processes into several cycles. The main objective of the latter is to limit the waste of time and energy by limiting the number of production tasks to be carried out.
While Scrum is adapted to the management of a single project, Kanban is better suited to the management of several projects or to TMA (third-party application maintenance) and MCO (maintenance in operational condition).
Scrum vs Safe
If Scrum remains the most popular agile method at the moment, it is followed by other methodologies that are more and more efficient in terms of agility. This is particularly true of the Scaled Agile Framework, more commonly known as Safe, which allows for more flexible work management in large companies.